
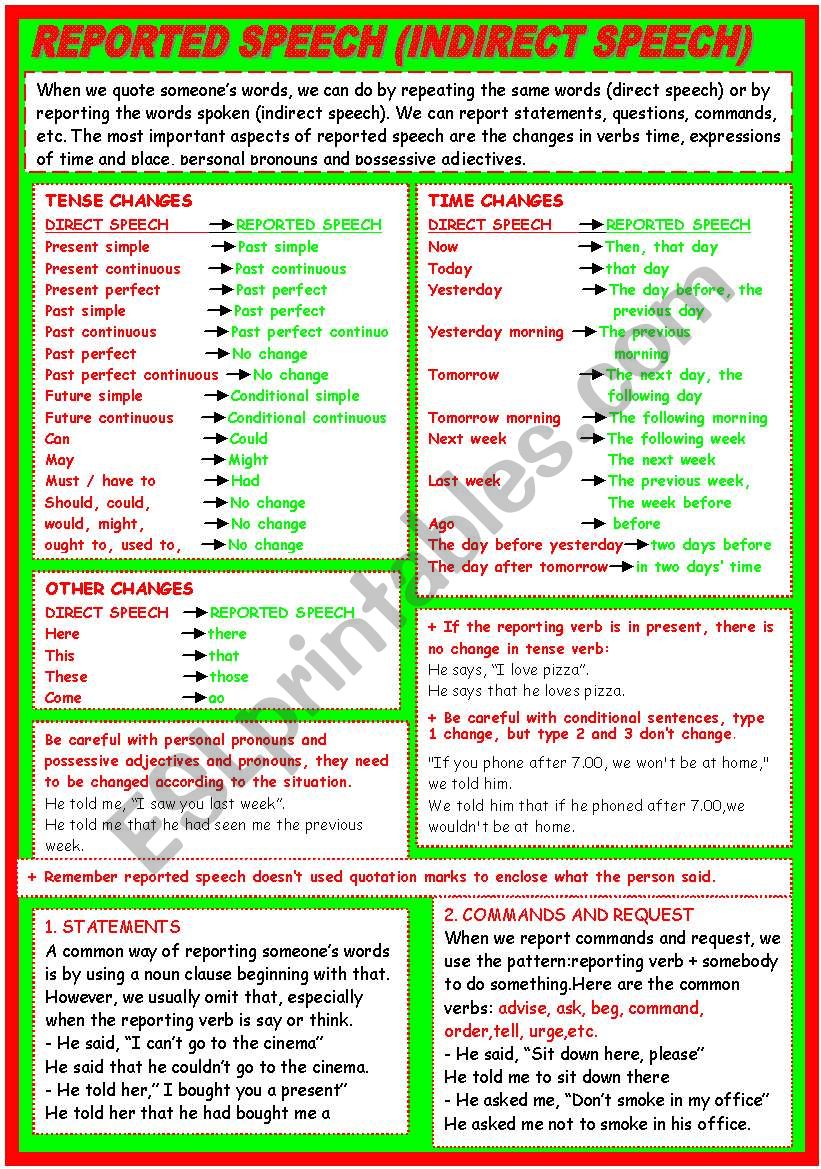
The police officer warned us not to go in there.The guide told us to wait for her in reception.We can also use an infinitive to report imperatives, with a reporting verb like tell, order, instruct, direct or warn. They advised us not to write our passwords down.'It's not a good idea to write your passwords down.' She promised to do the report by Friday.'I'll do the report by Friday, for sure.' Verbs like advise, agree, challenge, claim, decide, demand, encourage, invite, offer, persuade, promise, refuse and remind can follow an infinitive pattern. Many reporting verbs can be followed by another verb in either an infinitive or an -ing form. However, we can also use other reporting verbs. When we tell someone what another person said, we often use the verbs say, tell or ask. Reported speech 3 – reporting verbs: 1 Grammar explanation Indirect speech: He denied finishing the coffee. Indirect speech: He told us to wait there.ĭirect speech: 'It wasn't me who finished the coffee,' he said. Indirect speech: She persuaded me to come. 'Would you like me to help you?'ĭo this exercise to test your grammar again.Look at these examples to see how reporting verbs are used.ĭirect speech: 'You should come, it's going to be a lot of fun,' she said. If the question is making an offer, request or suggestion, we can use a specific verb pattern instead, for example offer + infinitive, ask + infinitive or suggest + ing. He wondered when we could get it done by.She wanted to know if they'd brought their passports.The most common reporting verb for questions is ask, but we can also use verbs like enquire, want to know or wonder. In what, where, why, who, when or how questions, we use the question word to report the question. She asked us whether we'd finished the project yet.He asked me if I was going to the Helsinki conference.'Are you going to the Helsinki conference?' In yes/ no questions, we use if or whether to report the question. You can learn about these changes on the Reported speech 1 – statements page. We also often make changes to the tenses and other words in the same way as for reported statements (e.g. Do you like) to a statement structure (e.g. In indirect speech, we change the question structure (e.g.
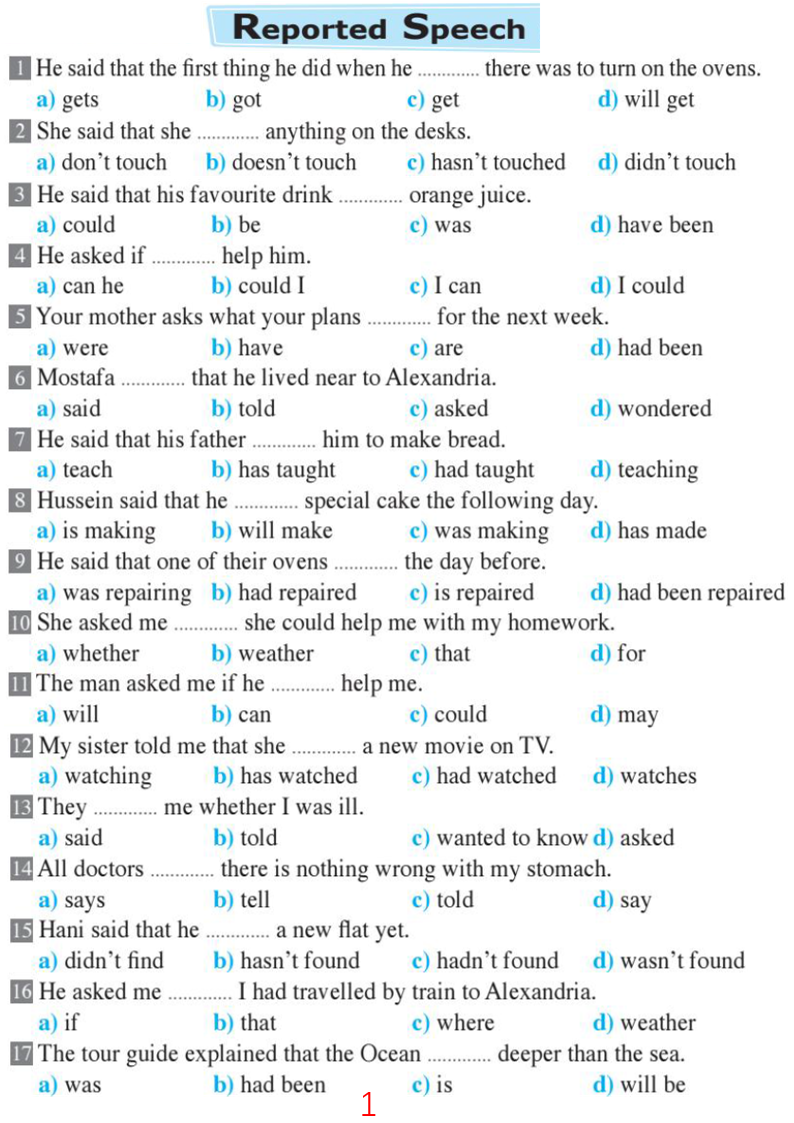
Indirect speech: He asked me if I liked working in sales. To do this, we can use direct speech or indirect speech.ĭirect speech: 'Do you like working in sales?' he asked. Grammar explanationĪ reported question is when we tell someone what another person asked. Indirect speech: She asked me to write it down. Indirect speech: She asked me who I'd seen.ĭirect speech: 'Could you write that down for me?' she asked. Indirect speech: He asked me if I worked from home.ĭirect speech: 'Who did you see?' she asked. direct speech: 'Do you work from home?' he said. Look at these examples to see how we can tell someone what another person asked.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
